Since its manifestation, the coronavirus pandemic has had an overwhelming impact and is poised to have a lasting effect on the economy. Although some major shifts may be a direct result of the pandemic, many will be due to amplification of industry trends that had been transforming the market for a number of years. For example, as market share continues to become increasingly concentrated among a few companies within industries, the shift towards industry consolidation will likely intensify.
Significant factors leading to consolidation include: mergers & acquisitions (M&A), rising corporate bankruptcies, significant balance sheet disparities, strong brand power, growing preference for industrial policies and acceleration of digitalization and associated network effects. Many of these factors tend to favor companies already pronounced within their industries, as their size and ability to generate significant sums of cash (when compared to their smaller counterparts) enables them to continue investing in long-term growth opportunities like research & development (R&D) and M&A. This strategic advantage provides these established companies with an opportunity to create greater returns internally and for shareholders.
In this Post-Crisis Industry & Equity Market Concentration report, Carleton McKenna provides further insights into the factors that have driven current consolidation trends, as well as those that will likely play larger roles in driving growth and increasing returns coming out of the pandemic.
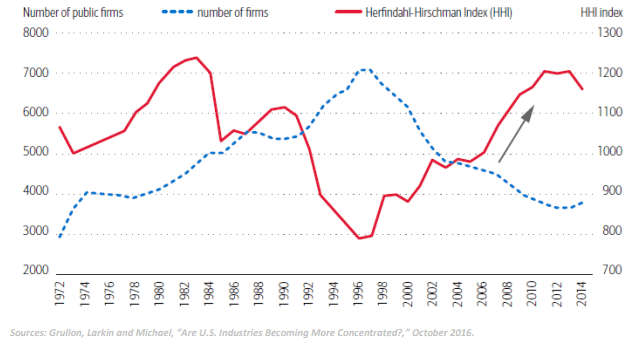
Market Concentration Vs. Number of Firms
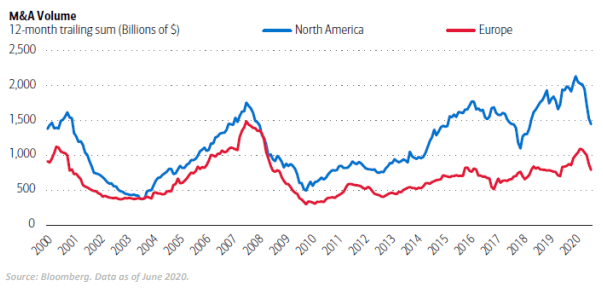
More M&A Following COVID-19 Could Lead to Greater Consolidation
M&A volume is currently down approximately 50% YTD as a result of the coronavirus pandemic, with some deals delayed or pulled back entirely. That said, there is likely to be a renewed push for M&A once management teams gain confidence in the economy reopening. Some of the major factors expected to drive M&A demand include strong cash balances, potentially favorable valuations and an acceleration of the digital economy as companies adapt to shifts in consumer demand. Companies that were previously slow to adopt or develop digital technologies will look to quickly acquire rather than build. Companies with an already strong digital presence will look to maintain their position by buying out competitors or acquiring parts of their supply chain.
Strong Balance Sheets are Expected to Prove Resilient
Smaller companies tend to carry more debt on their balance sheets, restricting access to capital markets. Large companies with strong balance sheets are generally better equipped to maintain investments in R&D throughout the business cycle, which can ultimately lead to outperformance and increased market share. Even prior to the pandemic, cash balances were becoming increasingly concentrated across large firms. In 2019, 40% of non-financial cash holdings were held by the top seven mega-caps—up from 20% in 2009.
To date, government stimulus has softened the pandemic impact for small- and medium-size firms; however, many could continue to struggle depending on how the pandemic progresses through the remainder of 2020.
Cash Giants: M&A and R&D Trends
- Although overall U.S. M&A has slowed YTD 2020, the 5 largest tech companies have announced 19 deals — their fastest pace since 2015.
- While general R&D investments in the U.S. were up only 3% YoY in Q1 2020, the 5 largest tech companies have increased R&D spending by 17%.
Source: Bank of America Corporation
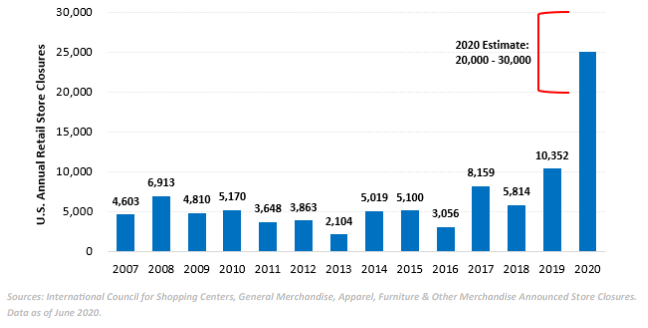
Bankruptcies Could Accelerate and Contribute Further to Consolidation
According to the June 2020 edition of the Financial Times, 3,427 companies have filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in the U.S. YTD 2020, numbers that have not been seen since the Great Recession (e.g., retail store closures are expected to total between 20,000 and 30,000 by the end of the year). While distressed companies struggle to survive, stronger, established companies are expected to gain further market share.
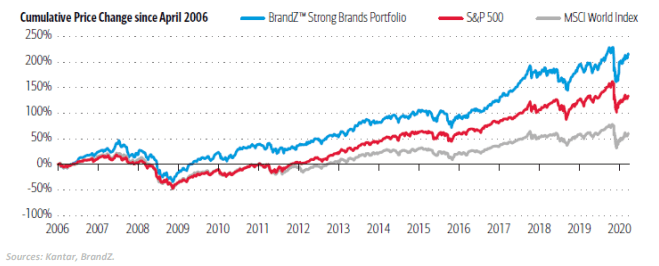
Strong Brands are Expected to Emerge Stronger Following COVID-19
As shown in the image above, companies with superior brand power typically have better access to credit markets and tend to rebound faster following recessionary periods. This implies that large-cap, established and trusted brands may gain more market share and more easily build on existing customer loyalties.
Acceleration of the Digital Economy May Lead to Greater Network Effects
Platform companies (e.g., e-commerce providers, social media networks, digital payment platforms, etc.) tend to benefit from increases in scale as value of service directly relates to the number of users on the platform. The more users that join, the more value that is created, enticing more people to sign up for the platform. Consumer data collected is used to power algorithms and artificial intellegence programs that more effectively personalize consumer experience for ad-targeting and user-interface preference.
Market Concentration: Industry Breakdown
The top 4 companies within the following industries hold over 80% of market share:
- Drugstore Chains;
- Home Improvements;
- Motor Vehicles;
- Integrated Oil;
- Computer Hardware;
- Food Retail;
- Internet Retail;
- Medical Distributors;
- Air Freight Couriers;
- Telecom Equipment;
- Telecom Providers;
- Multi-Line Insurance;
- Oil Refining/Marketing;
- Managerial HealthCare;
- Internet Software Services;
- Airlines; and
- Cable/Satellite/TV.
Concluding Thoughts:
As the coronavirus pandemic continues to affect business operations, the trend of consolidation across and within industries is expected to increase. Large firms with strong balance sheets are better equipped to handle recessionary periods, maintaining the cash necessary to make strategic moves while investing in R&D. Additionally, companies with strong brand recognition and valuable intangible assets are well-suited to emerge from the pandemic stronger than before, as they typically have better access to credit markets and can leverage existing customer loyalties.